⚛⚛⚛⚛⚛⚛⚛⚛⚛
✔️ INFOGEST main goals
➡️ The INFOGEST network aims at building an open international network of institutes undertaking multidisciplinary basic research on food digestion gathering scientists from different origins (food scientists, gut physiologists, nutritionists...)
➡️ INFOGEST targets the following main scientific goals :
↪️ Elucidating the relationship between food structure and food components’ bioavailability
↪️ Understanding the effect of processing on benefi cial food components’ bioavailability• Developing a multi-scale characterisation of food structures
↪️ Harmonising in vitro digestion models at the European levelReader’s digestA multidisciplinary, international project – which, amongst other things, is currently researching the relationship between the structure of food (fruits and vegetables, meat, dairy and egg products) and their digestion in the gastrointestinal tract – promises exciting results and novel technology, with potentially groundbreaking consequences
↪️ Validating in vitro digestion models against experimental human data
↪️ Creating an international database of bioaccessible food digestion products
↪️ Improving knowledge of the relationship between protein digestibility and allergenicity
↪️ Demonstrating the effect of food protein digestion on satiety and satiation• Increasing knowledge on the modulation of the human microbiota by food proteins
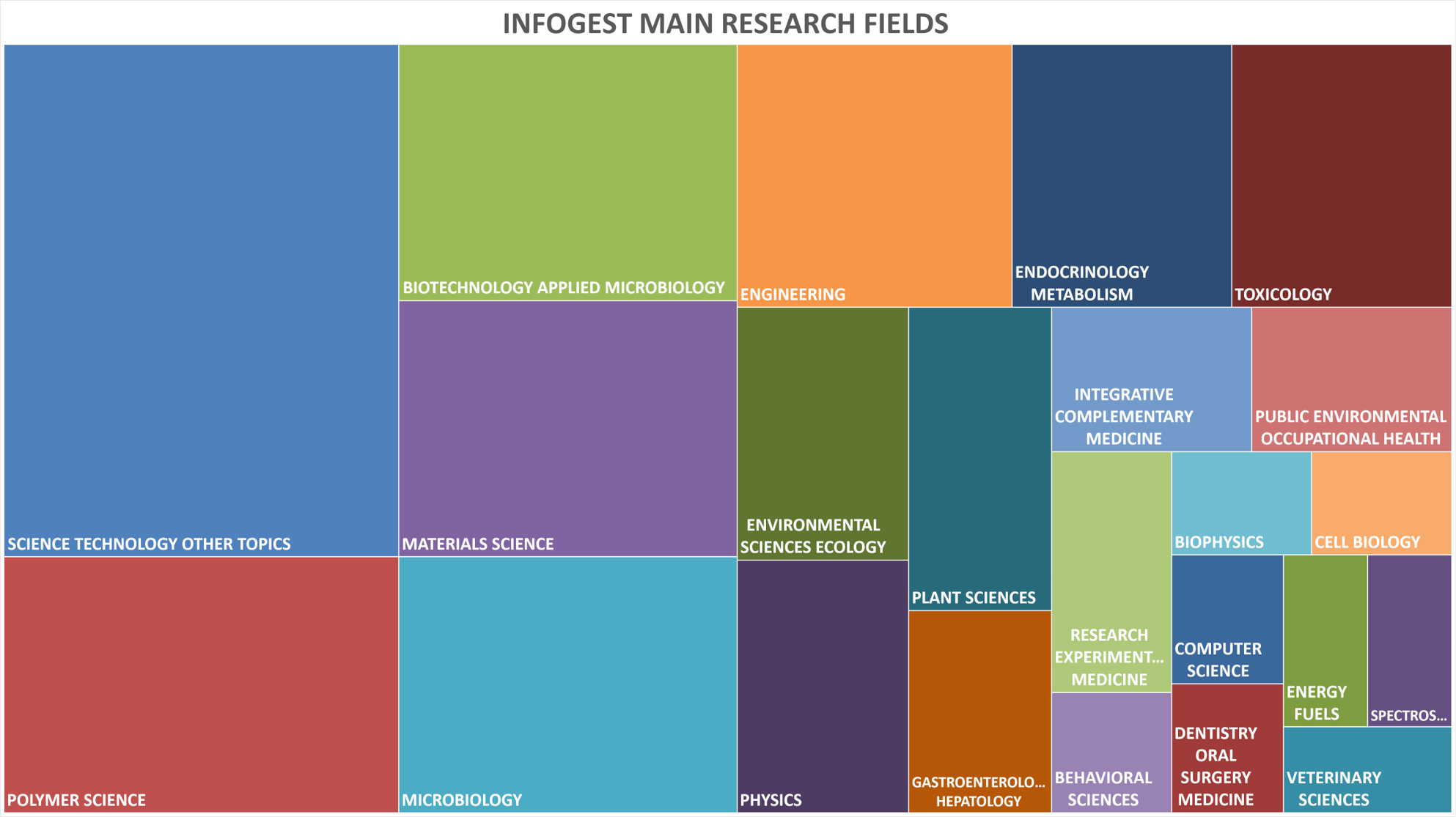
➡️ For this purpose, INFOGEST is implied in 23 main research fields, from applied microbiology to science technology, plant sciences, health and medecine.
⚛⚛⚛⚛⚛⚛⚛⚛⚛
✔️ Major outcomes of the Network so far
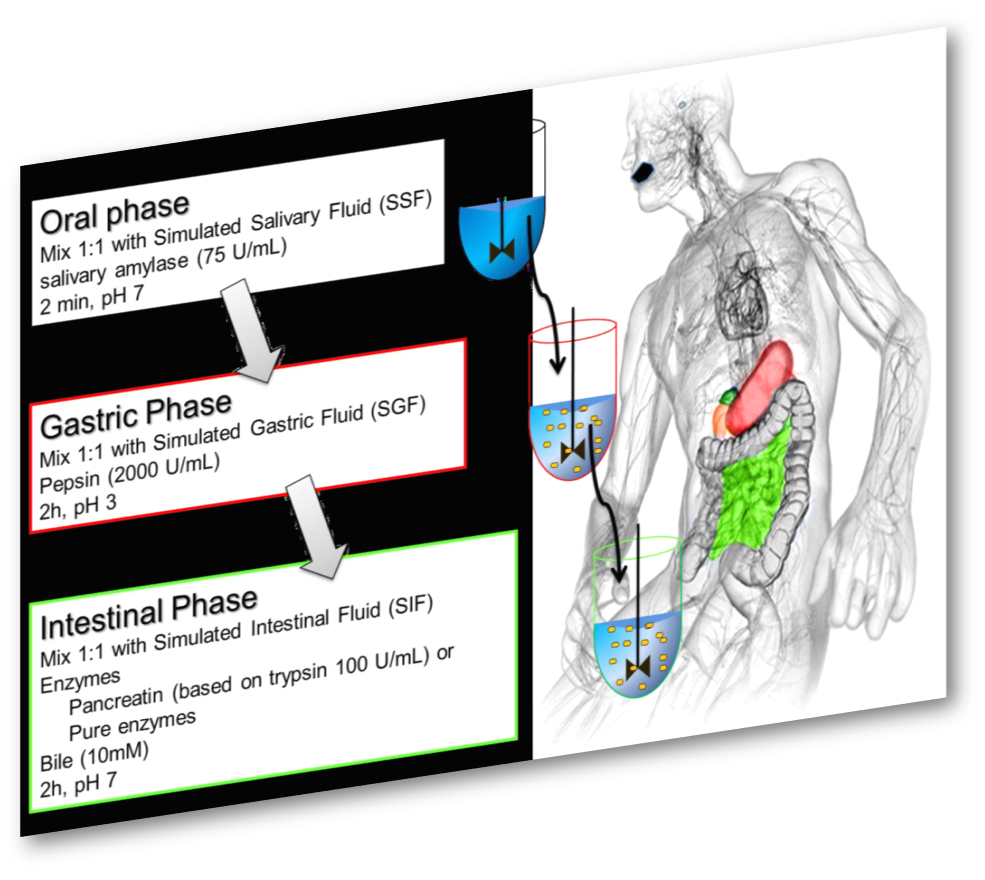
➡️ INFOGEST allowed the harmonization of the methodologies used to study digestion and proposed guidelines for performing new experiments. One of the major outcomes of the Network was the release and publication of a consensus model of in vitro digestion that has been cited more than 3000 times since 2014 and has been updated in a paper released by Nature Protocols.
⚡ The In vitro gastro-intestinal digestion Consensus INFOGEST protocol ⚡
↪ Citation of the original INFOGEST digestion method (Click on to access to the open access pdf file):
Minekus, M. and Alminger, M. and Alvito, P. and Ballance, S. and Bohn, T. and Bourlieu, C. and Carrière, F. and Boutrou, R. and Corredig, M. and Dupont, D. and Dufour, C. and Egger, L. and Golding, M. and Karakaya, S. and Kirkhus, B. and Le Feunteun, S. and Lesmes, U. and Macierzanka, A. and Mackie, A. and Marze, S. and McClements, D. J. and Ménard, O. and Recio, I. and Santos, C. N. and Singh, R. P. and Vegarud, G. E. and Wickham, M. S. J. and Weitschies, W. and Brodkorb, A. A standardised static in vitro digestion method suitable for food – an international consensus (2014), Food Funct. 5(6), 1113-1124
➡️ An amended and improved digestion method (INFOGEST 2.0) is being published in Nature Protocols in January 2019. This updated protocol addresses a number of ambiguities in the original scheme such as the inclusion of the oral phase and the use of gastric lipase.
↪ Citation of the INFOGEST 2.0 improved digestion method (Click on to access to the open access pdf file):
Brodkorb A, Egger L, Alminger M, Alvito P, Assunção R, Ballance S, Bohn T, Bourlieu-Lacanal C, Boutrou R, Carrière F, Clemente A, Corredig M, Dupont D, Dufour C, Edwards C, Golding M, Karakaya S, Kirkhus B, Le Feunteun S, Lesmes U, Macierzanka A, Mackie AR, Martins C, Marze S, McClements DJ, Ménard O, Minekus M, Portmann R, Santos CN, Souchon I, Singh RP, Vegarud GE, Wickham MSJ, Weitschies W, Recio I. INFOGEST static in vitro simulation of gastrointestinal food digestion. Nat Protoc. 2019 Apr;14(4):991-1014. doi: 10.1038/s41596-018-0119-1. Epub 2019 Mar 18. PMID: 30886367.
↪ Video illustration from the INFOGEST youtube channel (all details HERE):
- A step-by-step description of the standardised INFOGEST static in vitro digestion method for food, based on an international consensus developed by the COST INFOGEST network.
- The method is designed to be used with the standard laboratory equipment and limited experience to encourage a wide range of researchers to adopt it.
- It is a static digestion method that uses constant ratios of meal to digestive fluids and a constant pH for each step of digestion.
- The method can be used to assess the end points resulting from digestion of foods, to analyse the digestion products (e.g. peptides/amino acids, fatty acids, simple sugars, etc.) and evaluate the release of micronutrients from the food matrix. The whole protocol can be completed in ~7 days including ~5 days required for determination of enzyme activities.
➡️ New models are also being studied, and are the subject of significant advances:
↪️ A first step towards a consensus static in vitro model for simulating full-term infant digestion
↪️ Static in vitro digestion model adapted to the general older adult population: an INFOGEST international consensus
↪️ A standardised semi-dynamic in vitro digestion method suitable for food – an international consensus
➡️ The model is now used all around the world and can be learned through videos available on a YouTube channel specifically created for the Action with more than 15000 views in 4 years.
➡️ Beside an increased knowledge on the digestive process that is now shared among all the participants, the other outcomes were :
- The validation of in vitro models towards in vivo data (animal and human)
- The identification of bioactives released in the gut during digestion (databases available)
- The demonstration of the impact of the structure of food on its disintegration in the gut
- The bioavailability of food nutrients and bioactives
- A better knowledge on the relationship between food and human health
⚛⚛⚛⚛⚛⚛⚛⚛⚛
✔️ Five ring-trials have been organized within the network for :
- Comparing different models of in vitro digestion on the dairy sample,
- Checking the effect of processing on the digestion of meat and pasta,
- Characterizing food by multi-scale (from the molecular to the macroscopic level) strategy.
⚛⚛⚛⚛⚛⚛⚛⚛⚛
✔️INFOGEST advances
➡️ INFOGEST has funded 36 staff exchanges between partners for a total of 100 months spent abroad.
➡️ INFOGEST has created the International Conference of Food Digestion (7 issues between 2012 and 2021) that is now regularly followed by more than 250 scientists. It had a strong leverage effect with more than 80 national and international spin-off projects allowing to raise more than 54M€ of funding for the participants.
➡️ Around 544 peer-reviewed publications involving at least 2 different partners from INFOGEST have been released, whereas an open access 341-page book has reviewed all the in vitro and in vivo tools available.
➡️ INFOGEST has established strong connections between academic and industry partners. Indeed, more than 55 private companies (SMEs as well as large groups), mainly from the food sector, have been involved in the Network allowing to initiate joint projects.
➡️ Finally, INFOGEST has strong connections with the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) and is often questionned about digestion models that could be used to predict allergenicity of new proteins.
⚛⚛⚛⚛⚛⚛⚛⚛⚛